[ad_1]
Medicare and Medicaid supply well being protection to 12.5 million people who are enrolled in each techniques, referred to as “dual-eligible people.” Medicare is their number one supply of medical health insurance protection, and Medicaid, collectively funded via federal and state governments, supplies supplemental protection. Below the extensive umbrella of Medicare protection, dual-eligible people may also be lined beneath a number of other preparations, together with conventional Medicare, Medicare Benefit plans which are to be had to all Medicare beneficiaries, and plans which are designed particularly for this inhabitants (referred to right here as “dual-eligible plans”).
In combination, Medicare and Medicaid quilt a variety of products and services and monetary helps to lend a hand meet the varied wishes of the dual-eligible population, which is extra racially and ethnically numerous, and much more likely to be ill than Medicare beneficiaries with out Medicaid. On the identical time, there are ongoing issues a couple of loss of integration of products and services around the two techniques that can give a contribution to fragmentation of care, poor outcomes, and excessive prices. In keeping with those issues, federal and state lawmakers were operating to expand, take a look at and put into effect a number of protection and financing choices to reinforce coordination of deal with this inhabitants.
To tell attention of those protection and financing choices, together with what they could imply for the way dual-eligible people get their Medicare and Medicaid advantages, and who could be most influenced, this temporary items nationwide and state-level resources of Medicare protection for dual-eligible people, via demographic traits, according to the 2020 Medicare Beneficiary Abstract Document (See Strategies for main points and Appendix Desk 1).
Key takeaways:
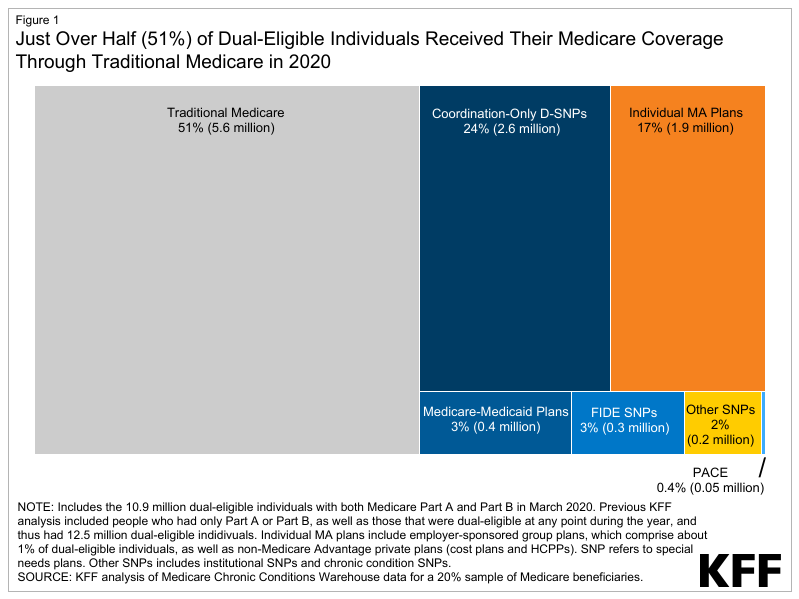
- Simply over part (51%) of dual-eligible people gained their Medicare advantages via conventional Medicare in 2020, whilst the remainder 49% had been enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans (Determine 1).
- 3 in 10 (30%) dual-eligible people had been enrolled in a dual-eligible plan, maximum of whom (24%) had been in coordination-only twin eligible particular wishes plans (D-SNPs). Coordination-only D-SNPs are designed for dual-eligible people and are required to coordinate with state Medicaid techniques, with some variation within the explicit necessities throughout states.
- Enrollment of dual-eligible people in conventional Medicare ranged from not up to 30% in Hawaii and Puerto Rico to 70% or over in 11 states (Alaska, Delaware, Maryland, Montana, North Dakota, New Hampshire, Oklahoma, South Dakota, Vermont, West Virginia, and Wyoming).
- Amongst dual-eligible people, Medicare Benefit enrollment charges had been upper amongst beneficiaries who had been age 65 and older than the ones beneath age 65 (53% vs 41%) and amongst beneficiaries who had been Black (54%), Hispanic (65%), and Asian/Pacific Islander (48%) than non-Hispanic White beneficiaries (41%).
Determine 1: Simply Over Part (51%) of Twin-Eligible People Won Their Medicare Protection Via Conventional Medicare in 2020
Assessment of Medicare Protection Choices for Twin-Eligible People
Like any Medicare beneficiaries, dual-eligible people might make a selection to obtain their Medicare advantages via conventional Medicare or a Medicare Benefit plan. This resolution could have implications for the way dual-eligible people obtain their Medicaid advantages and the level to which that protection is coordinated with Medicare. State Medicaid techniques quilt advantages that Medicare does no longer quilt, comparable to long-term products and services and helps and non-emergency transportation, in addition to a broader set of behavioral well being products and services via Medicaid fee-for-service or Medicaid managed care. Most (73%) dual-eligible persons are eligible for the total vary of Medicaid advantages no longer another way lined via Medicare and are known as “full-benefit” dual-eligible people. Medicaid additionally supplies maximum full-benefit dual-eligible people top class and in lots of instances, cost-sharing help during the Medicare Financial savings Program. “Partial-benefit” dual-eligible people aren’t eligible for complete Medicaid advantages however are eligible for help with Medicare premiums and, in lots of instances, charge sharing, additionally during the Medicare Financial savings Methods.
The quite a lot of Medicare protection choices for dual-eligible persons are summarized under and in Appendix Desk 1.
Conventional Medicare
In conventional Medicare, beneficiaries can download care from any supplier that participates in Medicare. The cost and supply of care in conventional Medicare has developed over the past a number of a long time, with cost together with a mixture of fee-for-service, bundled, and potential bills, in addition to value-based cost fashions, comparable to Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs). ACOs are a bunch of medical doctors, hospitals and suppliers that shape partnerships to be jointly liable for the care coordination in their sufferers.
Medicare Benefit
Medicare Benefit plans obtain a cost from the government to ship Medicare Section A and Section B advantages, and, generally, Section D drug protection. Medicare Benefit plans continuously supply some protection of supplemental advantages, comparable to imaginative and prescient and dental. Those plans are authorized to restrict supplier networks and might require prior authorization for positive products and services or referrals for positive kinds of suppliers. On this temporary, all non-public plans are known as Medicare Benefit plans, together with charge contract plans, well being care prepayment plans, Program of All-Inclusive Maintain the Aged, and Medicare-Medicaid plans. Medicare Benefit plans were categorised into dual-eligible plans and non-dual-eligible plans (described under).
Twin-eligible plans
On this temporary, dual-eligible plans are outlined as non-public plans or techniques which are designed for people who find themselves dually enrolled in Medicare and Medicaid and, to various levels, coordinate advantages around the two techniques. Twin-eligible people aren’t required to sign up for a dual-eligible plan, even supposing in some states, Medicare-Medicaid plans (MMPs) and entirely built-in dual-eligible (FIDE) SNPs be able to passively sign up dual-eligible people, because of this people would want to opt-out if they like a unique Medicare protection association. Financing of dual-eligible plans additionally varies throughout plan sorts, and continuously inside of plan sorts relying at the level of coordination in protection and advantages.
On this research, dual-eligible plans come with:
- Twin eligible particular wishes plans (D-SNPs) are one of those Medicare Benefit plan that supply Medicare protection and might coordinate or quilt Medicaid advantages relying on the kind of D-SNP. D-SNPs have contracts with the government to supply protection to Medicare beneficiaries and obtain a capitated cost to hide the price of all Medicare-covered products and services and supplemental advantages integrated within the plan. When supplemental advantages reproduction Medicaid-covered advantages, the Medicare cost covers those prices. D-SNPs are required via Medicare to have contracts with Medicaid techniques within the states during which they perform and should meet minimum requirements, together with the ones associated with coordinating the supply of advantages with the Medicaid program. States be able to restrict enrollment in those plans to full-benefit dual-eligible people. There are 3 kinds of D-SNPs:
- Coordination-only D-SNPs should meet the minimal federal necessities however supply various ranges of coordination, relying on state necessities. Those D-SNPs supply Medicare-covered products and services and generally supplemental advantages, and the state Medicaid company or a Medicaid controlled care plan supplies Medicaid-covered products and services. Maximum D-SNPs fall into this class.
- Totally Built-in Twin-Eligible (FIDE) SNPs supply Medicare- and integrated Medicaid-covered products and services via a unmarried controlled care group. The similar group that gives the FIDE SNP should additionally be offering a Medicaid controlled care plan for any Medicaid advantages no longer integrated within the FIDE SNP. In some instances, positive Medicaid advantages could also be equipped via the state or via a unique well being plan. FIDE SNPs are paid via Medicare for Medicare-covered products and services and integrated supplemental advantages, and via Medicaid for Medicaid-covered products and services. It’s imaginable for folks to sign up for a FIDE SNP however no longer the better half Medicaid plan or vice versa. Beginning in 2025, FIDE SNPs might solely sign up full-benefit dual-eligible people if they’re enrolled in each the FIDE SNP and the Medicaid plan subsidized via the similar group.
- Extremely Built-in Twin-Eligible (HIDE) SNPs should meet the necessities of coordination-only D-SNPs and should actually have a Medicaid plan working in the similar counties because the D-SNP. The mum or dad group supplies each Medicare and Medicaid products and services, however there’s no requirement that the similar folks sign up in each plans. HIDE SNPs weren’t to be had till 2021 and aren’t integrated on this research.
- Medicare-Medicaid Plans (MMPs) had been established as an indication beneath the Financial Alignment Initiative the place a unmarried well being plan supplies all Medicare- and Medicaid-covered advantages. Enrollment in MMPs is restricted to full-benefit dual-eligible people. Contemporary regulations require that every one states finish their demonstration techniques of the MMP type via the top of 2025 and transition ultimate plans to HIDE or FIDE SNPs.
- Program of All-Inclusive Maintain the Aged (PACE) supplies complete scientific and social products and services to people who: (1) are 55 years of age or older, (2) want a nursing house point of care however can are living safely locally, and (3) are living in a PACE group provider space. The general public in PACE are dual-eligible people. PACE used to be made an enduring a part of the Medicare and Medicaid techniques via the Balanced Finances Act of 1997.
Non-dual-eligible plans
Non-dual-eligible plans are different Medicare Benefit and personal plans that can sign up dual-eligible people however don’t coordinate Medicare and Medicaid advantages. Those come with person Medicare Benefit plans which are most often to be had for enrollment to all folks with Medicare, team plans subsidized via employers and unions, and different SNPs for Medicare beneficiaries with specialised well being wishes, together with institutional particular wishes plans (I-SNPs) and protracted situation particular wishes plans (C-SNPs).
What percentage of dual-eligible people had been enrolled in conventional Medicare and Medicare Benefit plans?
Simply over part (51%) of all dual-eligible people had been in conventional Medicare and 49% had been enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans in 2020.
A smaller percentage of dual-eligible people had been enrolled in conventional Medicare than the percentage of Medicare beneficiaries with out Medicaid protection in conventional Medicare (51% vs. 57%, respectively) (Determine 2 and Appendix Desk 2).
Of the ten.9 million dual-eligible people enrolled in Medicare Section A and B in 2020, 5.6 million had been in conventional Medicare and 5.3 million had been enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans. Then again, amongst 5.3 million dual-eligible people enrolled in a Medicare Benefit plan, the bulk (61%) had been enrolled in a dual-eligible plan, and the remainder 39% had been in a non-dual-eligible plan (information no longer proven).
Amongst all dual-eligible people, 3 in 10 (30%) had been enrolled in dual-eligible plans (Determine 2). Enrollment in dual-eligible plans consisted essentially of enrollment in coordination-only D-SNPs (24%), adopted via MMPs (3%), FIDE SNPs (3%), and PACE (0.4%). Upper enrollment in coordination-only D-SNPs than different dual-eligible plan sorts is most probably pushed via higher plan availability, for the reason that different kinds of plans had been solely to be had in a restricted choice of states, and continuously in a subset of counties in 2020 (e.g., FIDE SNPs, 11 states; MMPs, 9 states; and PACE, 31 states).
About 1 in 5 (19%) dual-eligible people had been enrolled in a Medicare Benefit plan that used to be no longer designed for folks with each Medicare and Medicaid, essentially person Medicare Benefit plans to be had to all Medicare beneficiaries (17% of all dual-eligible people). Any other 2% had been in an I-SNP or C-SNP. In 2020, most of the people enrolled in I-SNPs (91%) had been dual-eligible people, whilst simply over one-quarter (26%) of enrollees in C-SNPs had been dual-eligible people.
In 37 states and the District of Columbia, a minimum of 50% of dual-eligible people gained their Medicare protection via conventional Medicare in 2020, together with 11 states the place 70% or extra of dual-eligible people had been in conventional Medicare (Determine 3). The proportion of dual-eligible people in conventional Medicare ranged from a excessive of 99% in Alaska to a low of 0.3% in Puerto Rico. The proportion of dual-eligible people in conventional Medicare throughout states used to be most often very similar to the percentage of Medicare beneficiaries with out Medicaid in conventional Medicare, except for in 6 states (Arizona, Florida, Hawaii, Rhode Island, South Carolina, and Tennessee) and Puerto Rico (Appendix Desk 2). As an example, in Arizona, 30% of dual-eligible people had been in conventional Medicare as opposed to 59% of Medicare beneficiaries with out Medicaid.
In 5 states (Arizona, Florida, Hawaii, Rhode Island, and Tennessee) and Puerto Rico, greater than 40% of dual-eligible people had been enrolled in a dual-eligible plan – upper than the nationwide percentage of dual-eligible people in a dual-eligible plan (30%). In 4 of those states, the somewhat excessive enrollment in dual-eligible plans used to be pushed via enrollment in coordination-only D-SNPs, together with Arizona (39%), Florida (43%), Hawaii (57%) and Tennessee (42%), whilst in Rhode Island, the enrollment in dual-eligible plans used to be very best in MMPs (33%). Against this, in 4 states (Maryland, Montana, North Dakota and Oklahoma), not up to 10% of dual-eligible people had been enrolled in a dual-eligible plan (Determine 3, Appendix Desk 3).
| Puerto Rico is integrated on this research of dual-eligible people in Medicare. Significantly, Puerto Rico’s Medicare and Medicaid techniques fluctuate from the 50 states and the District of Columbia. In Puerto Rico, just about all Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in a Medicare Benefit plan. Medicare Advantage penetration is upper throughout Puerto Rico than within the 50 states and District of Columbia. In 2023 a minimum of 90% of eligible Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in a Medicare Benefit plan throughout just about all Puerto Rican counties. Particularly, enrollment in D-SNPs accounts for a miles greater percentage of Medicare Benefit enrollment than in any of the 50 states or the District of Columbia.
Puerto Rico’s Medicaid program eligibility rules, benefits, delivery system and financing fluctuate in many ways from the ones within the 50 states and the District of Columbia. As an example, Puerto Rico does no longer quilt lots of the advantages that full-benefit dual-eligible people use comparable to long-term products and services and helps, and in Puerto Rico, cost-sharing help is equipped to full-benefit dual-eligible people, however to not partial-benefit dual-eligible people, as a result of Medicare Financial savings Methods aren’t to be had in Puerto Rico. |
The proportion of dual-eligible people in conventional Medicare and Medicare Benefit plans differed throughout subgroups of beneficiaries via race, age, and space of place of abode.
A bigger percentage of Black (54%), Hispanic (65%) and Asian/Pacific Islander (48%) dual-eligible people had been enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans than non-Hispanic White (41%) and American Indian/Alaska Local (25%) dual-eligible people. Decrease enrollment in coordination-only D-SNPs amongst non-Hispanic White people (16%) in comparison to Black (28%), Hispanic (37%) or Asian/Pacific Islander (24%) beneficiaries explains decrease total enrollment in Medicare Benefit plans amongst non-Hispanic White dual-eligible people.
A bigger percentage of dual-eligible people beneath age 65 gained their Medicare protection via conventional Medicare than dual-eligible people age 65 or older (59% vs 47%) (Determine 5). Upper enrollment in Medicare Benefit plans amongst dual-eligible beneficiaries age 65 or older in comparison to the ones beneath 65 (53% vs. 41%) is nearly completely accounted for via upper enrollment in person Medicare Benefit plans (20% vs 13%).
Two-thirds (67%) of dual-eligible people dwelling in rural spaces gained their Medicare protection via conventional Medicare in comparison to not up to part (48%) of dual-eligible people dwelling in metropolitan spaces. Conventional Medicare used to be additionally the extra not unusual supply of Medicare protection for dual-eligible people dwelling in a micropolitan space, the place 62% had been in conventional Medicare. As well as, a bigger percentage of dual-eligible people in metropolitan spaces had been enrolled in coordination-only D-SNPs (25%), FIDE SNPs (3%) and MMPs (4%) than dual-eligible people in micropolitan spaces (18%, 1% and 1%, respectively) and rural spaces (14%, 1% and zero.4%, respectively) (Determine 4).
A bigger percentage of full-benefit dual-eligible people had been in conventional Medicare than partial-benefit dual-eligible people.
Amongst dual-eligible people who gained complete advantages in 2020, just about 6 in 10 (55%) had been enrolled in conventional Medicare, whilst 45% had been enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans. For dual-eligible people receiving partial advantages, the trend used to be reversed, with 58% enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans and 42% in conventional Medicare (Determine 5).
3 in 10 (33%) full-benefit dual-eligible people had been enrolled in dual-eligible plans, in comparison to roughly 2 in 10 (23%) partial-benefit dual-eligible people. Amongst full-benefit dual-eligible people, enrollment in dual-eligible plans used to be in large part produced from enrollment in coordination-only D-SNPs (24% of full-benefit dual-eligible people), adopted via MMPs (5%), FIDE SNPs (4%), and PACE (1%). All partial-benefit dual-eligible people in dual-eligible plans had been in coordination-only D-SNPs, in large part because of enrollment restrictions in different dual-eligible plan sorts.
A smaller percentage of full-benefit dual-eligible people had been enrolled in non-dual-eligible Medicare Benefit plans than partial-benefit dual-eligible people (12% vs 35%). Amongst dual-eligible people receiving complete advantages, 10% had been in person Medicare Benefit plans, whilst amongst the ones receiving partial advantages, 34% had been in person Medicare Benefit plans.
In keeping with the entire enrollment patterns for full-benefit dual-eligible people, in maximum states (39) and the District of Columbia, greater than part of full-benefit dual-eligible people had been in conventional Medicare. Against this, in part of states (26), greater than part of partial-benefit dual-eligible people had been enrolled in Medicare Benefit plans (Appendix Desk 4).
Dialogue
In 2020, one 3rd (30%) of dual-eligible people had been enrolled in a Medicare Benefit plan designed for folks with each Medicare and Medicaid, 19% had been in some other Medicare Benefit plan, and simply over part (51%) gained their Medicare protection via conventional Medicare. The supply of Medicare protection for dual-eligible people numerous via state and via beneficiary traits.
Twin-eligible people have lower incomes, are extra racially and ethnically numerous, and continuously face higher psychological and bodily well being demanding situations than the overall Medicare inhabitants, which may make navigating the well being care machine and well being care protection difficult for this inhabitants. Separate eligibility necessities, advantages, and regulations for Medicare and Medicaid might additional give a contribution to what has been described as a “fragmented and disjointed machine of deal with twin eligibles.”
To deal with issues about fragmented care and excessive prices, some policymakers have proposed to make bigger the function of Medicare Benefit plans which are designed for dual-eligible people (or a subset of those plans). Current Medicare protection preparations for dual-eligible people range within the level of care coordination and integration of financing between Medicare and Medicaid. Some protection choices might be offering a greater degree of coordination and financing (comparable to FIDE D-SNPs) than others. Plans with most often upper levels of integration generally tend to have somewhat low enrollment national in comparison with the extra not unusual protection choices, partly as a result of they don’t seem to be broadly to be had.
Proposals that will require dual-eligible people to be lined beneath a Medicare Benefit plan designed for this inhabitants would imply a transition from one supply of Medicare protection to some other, doubtlessly disrupting care preparations between sufferers and suppliers relying on community restrictions, for the massive percentage of dual-eligible people who are lined beneath conventional Medicare – a bunch this is disproportionately non-Hispanic White, beneath the age of 65 with everlasting disabilities, dwelling in rural spaces, and dwelling in states the place enrollment in dual-eligible plans is these days somewhat low.
Upper enrollment amongst dual-eligible people in Medicare Benefit plans designed for this inhabitants may doubtlessly cope with fragmentation demanding situations between Medicare and Medicaid, regardless that according to present evidence, it’s not transparent those plans all the time reinforce the coordination of care. As well as, it’s not transparent how such adjustments would have an effect on expenditures beneath each techniques. Assessing the possible results of quite a lot of protection preparations at the reviews of dual-eligible people, and on Medicare and Medicaid spending is past the scope of this research however would tell attention of coverage proposals that goal to reinforce protection and deal with this high-need inhabitants.
This paintings used to be supported partly via Arnold Ventures. KFF maintains complete editorial keep an eye on over all of its coverage research, polling, and journalism actions.
[ad_2]
Source link

